Hodgkin Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that affects the lymphatic system which is a part of the immune system in the body. This type of cancer occurs when abnormal lymphocytes (a kind of white blood cells) increase in size and frequency which causes swelling of lymph nodes, as well as other signs. While it’s a grave disease, Hodgkin Lymphoma can be thought to be one of the most cureable cancers when it is detected early.
What is Hodgkin Lymphoma?
Hodgkin Lymphoma which is also referred to as Hodgkin’s Disease, is a form of cancer that affects the lymphatic system. The disease is distinguished through the appearance of Reed-Sternberg cell which are huge abnormal lymphocytes that can be seen under microscope. This distinctive characteristic distinguishes Hodgkin Lymphoma from other forms of lymphoma.
The lymphatic system comprises lymph nodes as well as spleen bone marrow, lymphatic vessels. Because the lymphatic system plays a major function in the immune system Hodgkin Lymphoma is a disease that can be a threat to multiple organs if it is not treated quickly.
Causes and Risk Factors
The Hodgkin Lymphoma’s exact cause isn’t fully identified, but a variety of factors can increase the risk of developing it:
-
Insufficiency of the immune system because of HIV or organ transplants.
-
Family family history of the lymphoma.
-
Viral diseases like Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
-
Genre and Age The most common gender and age group is in young adulthood (15-30 years) and among people older than 55. A little more prevalent in males.
Symptoms of Hodgkin Lymphoma
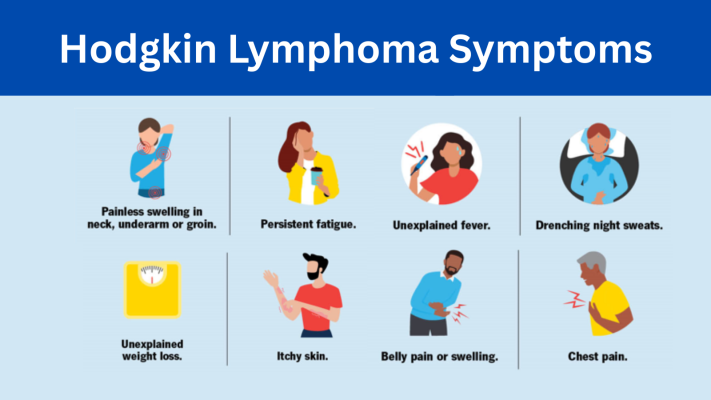
The early recognition of Hodgkin Lymphoma symptoms is essential for prompt treatment. Common signs include:
-
Lymph nodes that are swollen in the armpits, neck, or the groin.
-
Instant fatigue and weakening.
-
Frequent chills, fever as well as night sweats.
-
Weight loss that is not explained.
-
The skin is itchy, or there’s a an itch or.
-
Breathing difficulty or chest discomfort if lymph nodes within the chest become over-sized.
These symptoms can be a sign of other ailments, however persistent or advancing signs are not to be overlooked.
Types of Hodgkin Lymphoma
There are two major categories of Hodgkin Lymphoma.
-
Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (CHL):
-
The most well-known kind.
-
Subtypes Nodular Sclerosis, mixed cellularity, Lymphocyte-rich and Lymphocyte-depleted.
-
-
Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma (NLPHL):
-
A rarer type, typically developing slower.
-
Diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma
Diagnosis is a mix of medical assessment and tests that are specialized:
-
Physical exam The examination is for the presence of lymph nodes that are enlarged.
-
The blood tests to assess the overall health and function of the immune system.
-
Tests for image CT scans, PET scans and X-rays to assess the extent.
-
Lymph node biopsy confirms the presence of Reed-Sternberg cell.
-
Bone Marrow Biopsy is sometimes necessary to determine if disease has been able to spread.
Staging of Hodgkin Lymphoma
Staging aids doctors to determine the severity of the illness:
-
Stage 1: A single lymph node.
-
Stage 2: There are two or more lymph nodes areas on the same diaphragm.
-
Stage 3: Lymph nodes are affected both sides of the diaphragm.
-
stage 4: Expanding to various organs outside the lymphatic system.
Treatment Options for Hodgkin Lymphoma
The treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma depends upon the subtype, stage and general well-being of the person.
-
Chemotherapy
-
The most important treatment.
-
Make use of drug combinations like ABVD (Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine and Dacarbazine).
-
-
Radiation Therapy
-
Sometimes, chemotherapy is used in conjunction with.
-
Targets that affect lymph node regions.
-
-
Targeted Therapy
-
The drugs are designed to fight the cancer-specific protein or cell.
-
Example: Brentuximab vedotin.
-
-
Immunotherapy
-
The body’s immune system is stimulated to fight cancerous cells.
-
Examples: Immune checkpoint inhibitors like Nivolumab or Pembrolizumab.
-
-
Stem Cell Transplant
-
In relapsed and resistant cases.
-
Maintains bone marrow health following high dose chemotherapy.
-
Prognosis and Survival Rate
Hodgkin Lymphoma has a high survival rate in comparison to other cancers. Thanks to modern treatments:
-
Five-year rates of survival for the average is 87-90%..
-
Prognosis is improved in the beginning stages and for younger patients.
-
Treatment advances continue to improve the long-term results.
The Hodgkin Lymphoma
Controlling Hodgkin Lymphoma extends beyond medical treatment. Patients gain from:
-
Support for nutrition to keep the strength.
-
Support for psychological and emotional issues by counselling as well as support groups.
-
A regular follow-up to look out for any relapse or adverse effects.
Prevention and Awareness
At present, there is no guarantee of preventing Hodgkin Lymphoma. However, having an immune system that is strong and regular health checks aid in the early detection. Being aware of risks and symptoms can play a significant role in the timely detection.
Conclusion
Hodgkin Lymphoma is a serious but easily treated cancer that affects the lymphatic system. Thanks to advances in radiation, chemotherapy, stem cell transplants survival rates have dramatically increased. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and support can greatly improve the outcome of patients. Making people aware of Hodgkin Lymphoma is essential to ensure that more people can recognize the signs earlier and get medical treatment immediately.

