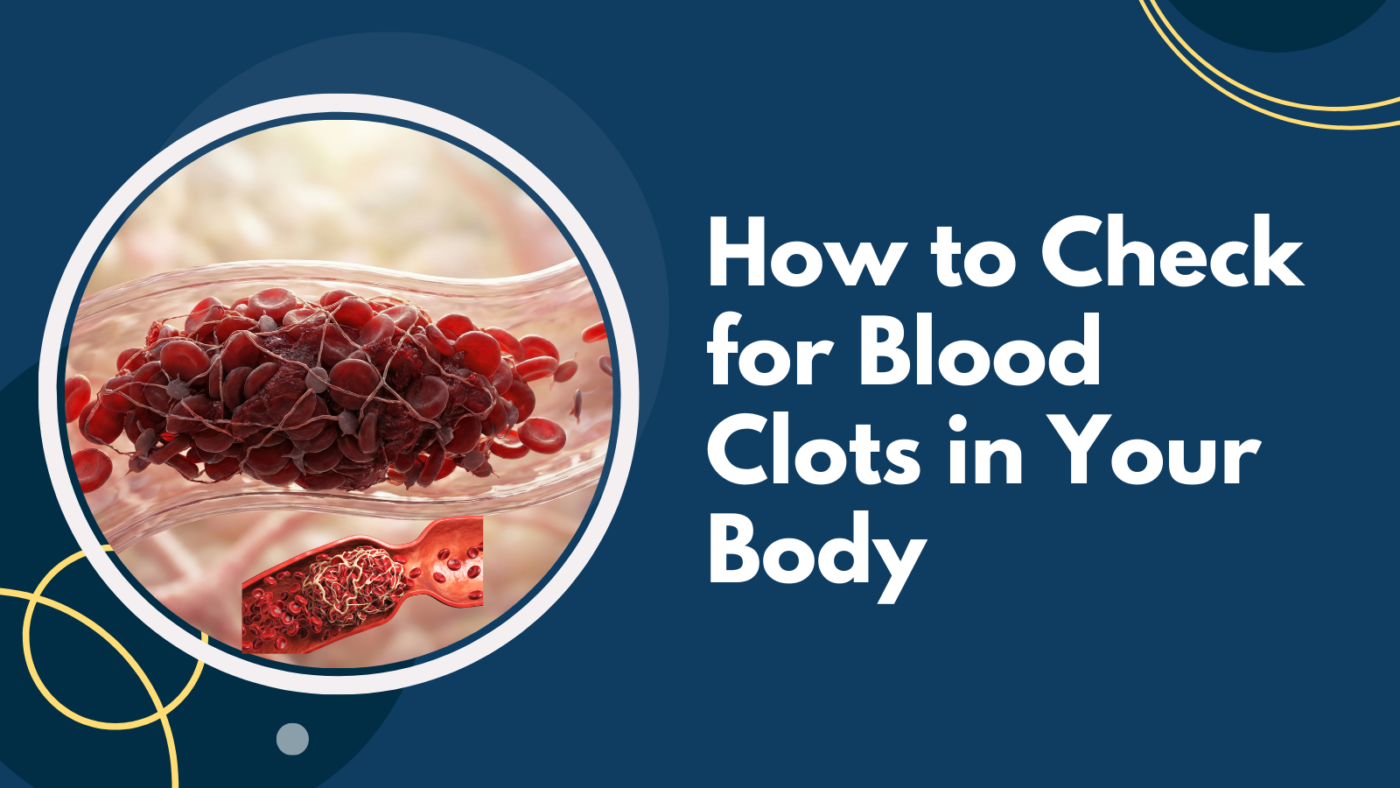
Blood clots play an essential role in stopping bleeding if you’re injured. But, if a formed clot is found within a blood vessel without any reason, or does not dissolve on its own, it can turn into a danger. Blood clots can impede the flow of blood, cause damage to organs, and in extreme instances, can be life-threatening. The early detection of clots is crucial but many aren’t sure what to do when blood clots appear or when it is time to seek medical attention.
This blog will explain how blood clots develop as well as the common warning signs that indicate it as well as diagnostic techniques and when it is time to see an expert.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood Clot is a clot that has a thickened layer of blood that develops when clotting proteins and platelets join. Normally, clots prevent excessive bleeding following an injury. Troubles occur when clots form within arteries or veins in the absence of injury, or fail to dissolve following healing.
The formation of blood clots is possible everywhere in the body but they usually form in:
-
Deep veins in leg veins (Deep Vein Thrombosis or DVT)
-
Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism – PE)
-
Brain
-
Heart
-
Abdomen
Why Blood Clots Are Dangerous
A blood clot may totally or partially stop the flow of blood. If a clot ruptures and circulates throughout the bloodstream, it could get stuck in vital organs like the lungs or the brain. This can cause severe complications, including heart attack, stroke or respiratory failure.
Since symptoms can be subtle or confused with different conditions, many blood clots are not detected until they cause severe harm.
Common Symptoms of Blood Clots
The signs of blood clots are based on the location where the clot is found. Being aware of these symptoms will allow you to seek prompt medical attention.
Blood Clots in the Legs (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
-
Swelling of the leg (rarely both)
-
Tenderness or pain, usually beginning in the calves
-
Warming over the affected area
-
Skin that is red or discolored
-
Leg cramps or heaviness
Blood Clots in the Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism)
-
Shortness of breath that is sudden
-
Pain in the chest that gets worse with deep breathing
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Coughing, occasionally with blood.
-
A fainting or lightheaded feeling
Blood Clots in the Brain
-
Sudden severe headache
-
Problems with vision
-
Trouble speaking
-
Numbness or weakness on an individual side
-
Lack of coordination
Blood Clots in the Heart
-
Pain in the chest or pressure
-
The pain can spread to the jaw, arm or the back
-
Nausea
-
Breathing shortness
-
Sweating
Blood Clots in the Abdomen
-
Abdominal pain severe
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Stool blood
-
Abdominal swelling
How Doctors Check for Blood Clots
There isn’t a single test that can detect every blood clot. Doctors use a mixture of medical history and physical exam, blood tests as well as imaging tests to establish the diagnosis.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step is understanding your signs and potential risk factors. Your physician may inquire about:
-
Recent hospitalization or surgery
-
Inactivity for long periods (bed repos, lengthy trip)
-
Hormone therapy or pregnancy
-
A family history of bleeding disorders
-
Smoking cigarettes or being overweight
-
Blood clots from the past
When conducting a physical examination, the doctor examines for tenderness, swelling or changes in the skin’s color and even warmth in the region.
2. Blood Tests (D-Dimer Test)
A D-dimer test determines the amount of a substance released when the blood clot is broken down. The presence of high levels could indicate an active clotting process within the body.
But, this test on its own does not confirm the presence of a blood clot. Increased levels of D-dimer can be caused by pregnancy, infection or recent surgery. It is used primarily to detect clots in those with low risk.
3. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is one of the popular test to identify blood clots within the legs. It makes use of sound waves to see the flow of blood through veins and to identify blockages.
This test involves:
-
Non-invasive
-
Painless
-
All are readily available
-
Highly effective in diagnosing DVT
4. CT Scan (CT Angiography)
A CT scan using contrast dye is typically used to identify clots in the abdomen, lungs, or in the brain. It gives clear photographs of blood vessels, and can help determine blockages.
CT scans can be extremely helpful in diagnosing arterial embolisms and pulmonary embolisms. blood clots.
5. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI can be used to identify blood clots within the spinal cord, brain or in certain abdominal vessels. It can provide high-quality images without radiation exposure, but it might not be appropriate for every patient.
6. Venography and Angiography
These imaging procedures are highly specialized and require injecting contrast dye into blood vessels, and then making pictures using X-rays. They are highly precise, however they are typically reserved for difficult or obscure instances due to their intrusive nature.
7. Echocardiogram
If you suspect a clot in the heart an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) can aid in assessing blood flow and reveal abnormalities in the body.
Who Is at Higher Risk of Blood Clots?
Certain conditions increase the chance to develop blood clots such as:
-
Long-term sitting or inactivity
-
Recent trauma or surgery
-
Treatments for cancer and cancer
-
Pregnancy and postpartum
-
Hormonal medication (oral contraceptives and hormone therapy)
-
Obesity
-
Smoking
-
Genetic clotting disorders
Anyone with risk factors should be aware of any symptoms.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
You should seek medical attention if you have:
-
Shortness of breath that is sudden
-
Chest pain
-
Sudden weakness or speech difficulty
-
Acute leg swelling or pain
-
The coughing up of blood
Blood clots are prone to advancing quickly The early detection of clots decreases the chance of risks.
Experiencing any of these symptoms? Book a consultation with Dr. Padmaja Lokireddy to get checked immediately.
Can Blood Clots Be Prevented?
Although no blood clots are able to be avoided, the chance is reduced through:
-
Physically active
-
Avoiding sitting for long periods of time
-
Drinking water is essential.
-
Controlling chronic conditions
-
Follow medical advice following surgery
-
Injecting prescribed blood thinners if recommended
Conclusion
Blood clots can be serious, but are they are often treated when they are detected early. Recognizing how to recognize warning signals and understanding the methods doctors use to check for blood clots will aid in taking appropriate action. If you notice any unusual symptoms or you have risk factors for clotting, you should not overlook these signs. An early diagnosis, timely testing and medical treatment can save your life.
If you suspect that there is a blood clot, contact your doctor immediately to get an assessment and direction.